Showing 1–12 of 27 results
-
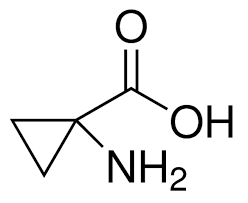
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid CAS:22059-21-8
Read more1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic Acid is a small molecule agonist at the glycine modulatory site of the NMDA receptor. Described to mimic the effects of glycine at the NMDAR, 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic Acid competitively inhibits binding of [3H]glycine and enhances the binding of [3H]MK-801 to NMDAR-coupled cation channels similarly to glycine (though with less efficacy). 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic Acid is shown to block convulsions and death produced by NMDA exposure, significantly reducing seizure induction and cell death of NMDA-treated hippocampal neurons.
-
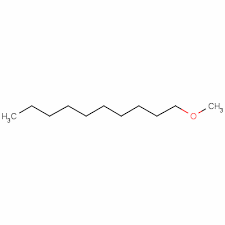
1-Methoxy Decane, Decyl Methyl Ether CAS: 7289-52-3
Read more1-Methoxy Decane | Decane,1-Methoxy | Decyl Methyl Ether Cas: 7289-52-3
Decyl Methyl Ether is a fragrance/Aroma compound with a fresh scent. Decyl Methyl Ether is a fatty ether used as a possible diesel fuel extender.
-
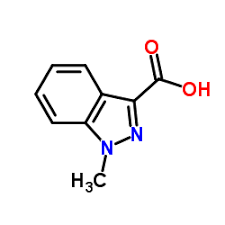
1-Methyl-3-indazolecarboxylic Acid
Read moreIndazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole.
-

3- Methyl 1,1- Diphenyl Urea
Read moreSynonyms:
3-Methyl-1,1-diphenylurea 13114-72-2 N’-METHYL-N,N-DIPHENYLUREA Urea,N’-methyl-N,N-diphenyl- N-methAKARDITE II -
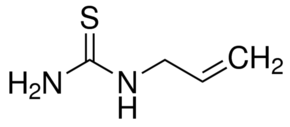
Allylthiourea
Read moreMolecular Formula C4H8N2S Synonyms ALLYLTHIOUREA
N-Allylthiourea
109-57-9
Thiosinamine
1-Allyl-2-thiourea
-

Ammonium Ceric Nitrate
Read moreIn organic synthesis, CAN is useful as an oxidant for many functional groups (alcohols, phenols, and ethers) as well as C–H bonds, especially those that are benzylic. Alkenes undergo dinitroxylation, although the outcome is solvent-dependent. Quinones are produced from catechols and hydroquinones and even nitroalkanes are oxidized. CAN provides an alternative to the Nef reaction; for example, for ketomacrolide synthesis where complicating side reactions usually encountered using other reagents. Oxidative halogenation can be promoted by CAN as an in situ oxidant for benzylic bromination, and the iodination of ketones and uracil derivatives.
-

Ammonium Reineckate Reineck salt
Read moreReinecke’s salt is a chemical compound with the formula NH4[Cr(NCS)4(NH3)2]·H2O. The dark-red crystalline compound is soluble in boiling water, acetone, and ethanol. The chromium atom is surrounded by six nitrogen atoms in an octahedral geometry. The NH3 ligands are mutually trans and the Cr–NCS groups are linear. The salt crystallizes with one molecule of water.
Properties Chemical formulaC4H12N7OCrS4 Molar mass 354.42 g/mol Appearance dark red solid Density 1.49 g/cm3 Melting point 270 °C (518 °F; 543 K) Boiling point decomposes Solubility in watersoluble in hot water -
Sale!

Basic Phenyl Mercury Nitrate CAS 8003-05-2
Original price was: ₹10,000.00.₹9,500.00Current price is: ₹9,500.00. Add to cart -

Benzene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-2,5-dinitroso CAS: 2140-40-2
Read moreBenzene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-2,5-dinitroso CAS: 2140-40-2 is special vulcanizing agent
-

Ceric Sulfate
Read moreCerium(IV) sulfate, also called ceric sulfate, is an inorganic compound. It exists as the anhydrous salt Ce(SO4)2 as well as a few hydrated forms: Ce(SO4)2(H2O)x, with x equal to 4, 8, or 12.
Uses:
The ceric ion is a strong oxidizer, especially under acidic conditions. If ceric sulfate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, then elemental chlorine is formed, albeit slowly. With stronger reducing agents it reacts much faster. For example, with sulfite in acidic environments it reacts quickly and completely.
When ceric compounds are reduced, so-called cerous compounds are formed. The reaction taking place is:
- Ce4+ + e− → Ce3+
The cerous ion is colorless.
